Gráficos de calamares gigantes
Published Monday, October 31, 2005 by Spyder.Estupendos gráficos interactivos que el diario El mundo ofrece en su edición digital, acerca de los calamares gigantes.
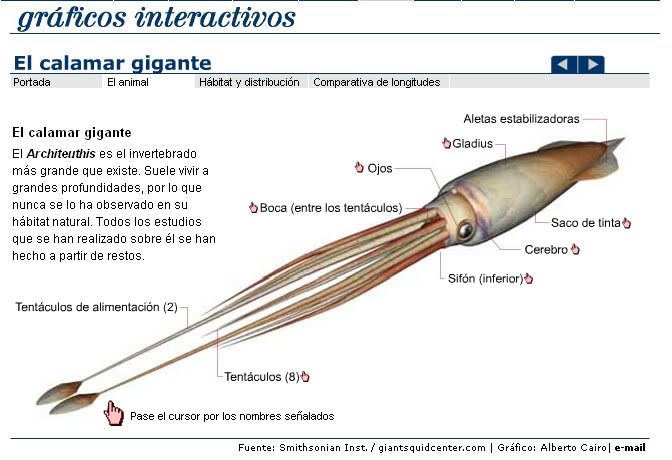

Labels: Monstruos marinos
Bulgakov -Diablo, margarita y pulpo-
Published Saturday, October 29, 2005 by Spyder."I felt, especially just before going to sleep, that some very cold, supple octopus was fastening its tentacles round my heart. I had to sleep with the light on.
'My beloved had changed too. I told her nothing about the octopus, of course, but she saw that something was wrong with me."
'My beloved had changed too. I told her nothing about the octopus, of course, but she saw that something was wrong with me."
En la versión original no sé como se titularía el libro en ruso, pero en españa fue traducido como
El diablo y Margarita, tal vez para darle un toque más moralizante a la novela.
El diablo y Margarita, tal vez para darle un toque más moralizante a la novela.
Mijaíl Bulgakov
Mijaíl Bulgakov Novelista y dramaturgo ruso Nació el 15 de mayo de 1891 en Kíev, Ucrania. Cursó estudios de Medicina aunque abandonó por la creación literaria. Sus primeras obras son: Maleficios (1925), Corazón de perro (1925), Morfina (1927) y El departamento de Zoia (1926). Con su novela La guardia blanca (1925) alcanzó el reconocimiento. A pesar de gozar de gran popularidad, las autoridades le prohibieron publicar a partir de 1930 por satirizar las costumbres soviéticas. Su obra maestra El maestro y Margarita (1966) fue escrita entre 1929 y 1940.
Vía buscabiografías
Labels: Literatura
Hentai tentacular
Published Thursday, October 27, 2005 by Spyder.Si ustedes han tenido la oportunidad de ver una película japonesa pornográfica editada para el mercado japonés se habrán dado cuenta con asombro que los primeros planos de los aparatos genitales quedan siempre difuminados con una mancha borrosa. Ocurre ello por un extraño sentido de la censura del país nipón que pese a permitir el consumo de películas o revistas pornográficas, éstas quedan totalmente “capadas”-
Esto también ocurre en los hentai (dibujos manga de alto contenido erótico), donde tampoco es demasiado bien visto el dibujo explícito de penes o de vello púbico. Sin embargo hecha la ley, hecha la trampa, y rápidamente un ejército de demonios tentaculares comenzaron a aparecer en los hentai y popularizarse entre esos lectores de manga. Los monstruos tentaculares de esta manera fueron ganando su espacio en el hentai, y además dieron rienda suelta a una serie de fantasía sexuales que siempre estuvieron presentes: la mujer dominada, la mujer penetrada por todos los lados (pues tentáculos nunca tienen por qué faltar), la mujer violada etc...

Via Wikipedia
Esto también ocurre en los hentai (dibujos manga de alto contenido erótico), donde tampoco es demasiado bien visto el dibujo explícito de penes o de vello púbico. Sin embargo hecha la ley, hecha la trampa, y rápidamente un ejército de demonios tentaculares comenzaron a aparecer en los hentai y popularizarse entre esos lectores de manga. Los monstruos tentaculares de esta manera fueron ganando su espacio en el hentai, y además dieron rienda suelta a una serie de fantasía sexuales que siempre estuvieron presentes: la mujer dominada, la mujer penetrada por todos los lados (pues tentáculos nunca tienen por qué faltar), la mujer violada etc...

Via Wikipedia
Legislación japonesa
El artículo 175 del código penal japonés prohíbe la publicación de material "moralmente perjudicial", que tal como se interpreta actualmente incluye la exposición de genitales, así que es frecuente ver una barra cubriendo los genitales, o bien los genitales borrosos. Antes de 1994, la interpretación de esta ley incluía la prohibición de exponer vello púbico, una norma que se eludía dibujando personajes sin vello púbico.
Sin embargo, esto ha causado otro problema cuando los vídeos hentai se distribuían a lugares como Europa y Estados Unidos. Como los personajes del anime parecen más jóvenes que los personajes de la misma edad de los dibujos animados occidentales, eso dio a algunos la impresión de que los vídeos contenían pornografía infantil. Es interesante saber que los personajes femeninos de los dibujos animados, según el japonés medio, aparentan tener unos 5 o 10 años más.
Un dato menos conocido es que la censura japonesa es muy estricta en cuanto a los dibujos sobre actividad sexual entre humanos y animales. Aunque se permite que circulen con relativa libertad actos con monstruos imaginarios (que suelen tener los conocidos tentáculos fálicos con el fin de evitar la ley relativa a los genitales de verdad), se ha considerado el sexo zoofílico con animales existentes como algo que debe ser perseguido.
Noticia -Calamares gigantes en el caladero de Carrandi-
Published Sunday, October 23, 2005 by Spyder.
El Caladero de Carrandi es una zona de pesca situada 25 millas al noroeste de Gijón, en la que frecuentemente se encuentran calamares gigantes. La presencia de estos y el interés creciente de los investigadores marinos sobre esta zona, han hecho que se comiencen a documentar exhaustivamente cada una de los nuevos ejemplares que aparecen muertos en las redes de los barcos pesqueros, así desde diciembre de 1999 hasta el presente se han documentado 14 ejemplares.

Aparecen nuevos ejemplares de Calamares de gran porte en la costa central Asturiana. El Caladero Carrandi sigue de actualidad.
Vía Colunga digital
El Cepesma comunicó el sábado 22-10-05 la aparición en aguas de la costa central asturiana , de dos ejemplares de especies singulares de calamar. El 112 fue advertido por pescadores deportivos de Salinas de sonidos en el agua que procedían de una especie rara de calamar que aún estaba vivo. Fue recogido ya muerto por miembros del Cepesma y trasladado a sus instalaciones en Luarca. Se trata de un calamar de la especie Thisanoteuthis rhombus de 14 kilogramos. Nunca se pescó ninguno similar en Asturias ya que es propio de aguas cálidas mediterraneas donde se le conoce como calamar rombo por la forma de sus aletas.
La continua aparición de calamares de grandes proporciones y otras especies raras cerca de aguas del Caladero Carrandi está contribuyendo a convertir esta zona en auténtico Santuario de los Calamares gigantes .
Hablando de Calamares gigantes este año se celebra el centenario de la muerte de ese gran visionario y escritor que fue Julio Verne quien ya nos hablaba de la existencia de estos seres gigantes de hasta 25 metros, en su novela 20.000 leguas de viaje submarino
Las leyendas del kraken, el cefalópodo gigante causante de naufragios, se conocen desde la antigüedad. Las pruebas científicas, por su parte, se remontan a finales del siglo XVIII. De ellas se valió el escritor francés para construir el monstruo de su novela de 1870, del que hoy nadie duda de su existencia.
Los calamares gigantes pueden medir hasta 19 metros, o más según los últimos estudios científicos. Muchos de los misterios sobre los calamares gigantes han perdurado a lo largo de los siglos. Se sabe que son grandes depredadores y que pueden tener neuronas de hasta un metro, pero todavía no han sido filmados en su propio medio, aunque recientemente un barco científico japonés a rodado alguna imagen de uno en aguas del Mar del Japón.
Por el momento, sólo han sido detectados kraken en Japón, Nueva Zelanda, Canadá y España (en Asturias, en el caladero Carrandi, frente a la costa colunguesa).

Aparecen nuevos ejemplares de Calamares de gran porte en la costa central Asturiana. El Caladero Carrandi sigue de actualidad.
Vía Colunga digital
El Cepesma comunicó el sábado 22-10-05 la aparición en aguas de la costa central asturiana , de dos ejemplares de especies singulares de calamar. El 112 fue advertido por pescadores deportivos de Salinas de sonidos en el agua que procedían de una especie rara de calamar que aún estaba vivo. Fue recogido ya muerto por miembros del Cepesma y trasladado a sus instalaciones en Luarca. Se trata de un calamar de la especie Thisanoteuthis rhombus de 14 kilogramos. Nunca se pescó ninguno similar en Asturias ya que es propio de aguas cálidas mediterraneas donde se le conoce como calamar rombo por la forma de sus aletas.
La continua aparición de calamares de grandes proporciones y otras especies raras cerca de aguas del Caladero Carrandi está contribuyendo a convertir esta zona en auténtico Santuario de los Calamares gigantes .
Hablando de Calamares gigantes este año se celebra el centenario de la muerte de ese gran visionario y escritor que fue Julio Verne quien ya nos hablaba de la existencia de estos seres gigantes de hasta 25 metros, en su novela 20.000 leguas de viaje submarino
Las leyendas del kraken, el cefalópodo gigante causante de naufragios, se conocen desde la antigüedad. Las pruebas científicas, por su parte, se remontan a finales del siglo XVIII. De ellas se valió el escritor francés para construir el monstruo de su novela de 1870, del que hoy nadie duda de su existencia.
Los calamares gigantes pueden medir hasta 19 metros, o más según los últimos estudios científicos. Muchos de los misterios sobre los calamares gigantes han perdurado a lo largo de los siglos. Se sabe que son grandes depredadores y que pueden tener neuronas de hasta un metro, pero todavía no han sido filmados en su propio medio, aunque recientemente un barco científico japonés a rodado alguna imagen de uno en aguas del Mar del Japón.
Por el momento, sólo han sido detectados kraken en Japón, Nueva Zelanda, Canadá y España (en Asturias, en el caladero Carrandi, frente a la costa colunguesa).
Labels: Monstruos marinos, Noticias
Arte y pulpos -Van Arno-
Published Saturday, October 22, 2005 by Spyder.

La imagen de superior está hecha por Van Arno, un artista de la noche, de esos que han vivido tantos excesos que lo normal ya no les satisface y buscan exagerar sus pinturas, hasta volverlas histriónicas, grotescas. Por un lado desprenden sexualidad, y por otro lado esa sexualidad se transforma en fealdad.
La página de Van Arno se puede visitar aquí.
Sus cuadros me recuerdan a una serie de fotografías del fotógrafo Erwin Olaf, a quién se debe la imagen inferior.
La página de Edwin Olaf se puede visitar aquí.
Van Arno
Van Arno was born in Chattanooga, Tennessee, in 1963, and grew up in St. Louis, Missouri, where he attended a Christian Science school from Kindergarten through High School.
He was accepted at Otis Parsons School of Design in Los Angeles, where he studied under Carol Caroompas and Lita Albquerque. Supporting himself working late nights as a bouncer in nightclubs and adult video arcades in mid 1980s LA.
As a young illustrator his work appeared on album covers, video game box art, and nightclub posters around the city. By the late eighties, he began producing large paintings blending cartoon imagery with portraits of cultural and historical icons. These early paintings used black lines and luridly cartoon color to depict characters ranging from John F. Kennedy to Herman Goering to Othello. His guerrilla installation of a 12 foot tall ANGEL could be seen hovering over Sunset Boulevard in Siverlake, Christmas 1992.
In the early 90s he became fascinated with the calendar of the ancient Maya, and traveled to Yucatan to see the ruins at Chichen Itza, Coba and Tulum. At the same time, he began to create heroic figurative works featuring religious and folk heroes from Christian, Mayan and American history (St. Francis, John Barrymore, Joan of Arc, Nat Turner, Nellie Bly) in cell vinyl on masonite. This work was shown extensively in Los Angeles, Seattle, Nashville and New York, and prominently featured his series of Olive Oyl paintings, inspired by his life-long fascination with the unattractive sexpot. A feature in Juxtapoz Magazine documented his work to date in January 1999. In the spring of 2000, several of his pieces were included in a national survey of Lowbrow painters at the Hollywood Art and Culture Center in Florida along with Mark Ryden, Chaz Bojorquez, Kenny Scharf, Sandow Birk and others. Van was pleased to speak at the opening to detail the history of lowbrow painting and its place in art history. In the fall of 2000, he painted a 36-foot billboard for the East Side Artcrawl entitled Abolitionist Goat War which received local news coverage for its indictment of pimp culture. In November, 2004, Van was honored to have a solo show in Hamburg, Germany, which was well covered in the local press because of growing interest in the JUXTAPOZ movement, and because of the re-election of George W. Bush, 3 days earlier. More recently, Van was introduced to oil painting by Robert Williams, and the classicism inherent in that medium has brought his work to a new level.
His ongoing fascination with the imagery of religion and its use of the heroic figure continues to find new relevance recently, as American Values are re-examined at home and abroad.
Although, he has been exploring non-narrative themes; recently, his focus remains on the figure, and its power to engage the viewer.
Erwin Olaf
Erwin Olaf, born in 1959 in The Netherlands, originally pursued a career in Journalism, attending the School for Journalism in Utrecht. There, he discovered photography and film.
Within the diversity of Olaf's subject matter - fashion, cinema, society, history, and advertising - he always achieves a very individual style. This is characterized by, on the one hand, making the personal public, creating unease as the protection of anonymity is drawn aside; and, on the other hand, extending the role of simple voyeur to that of transgressor. We feel his characters to be too intrusive, too close to us, and we imagine taking on their roles to become, for a moment, a porn star, a cruel clown or a martyred celebrity.
Labels: Artistas, Fotografías
El pulpo gigante en el Magic
Published Thursday, October 20, 2005 by Spyder.Hace una década comenzaron a verse las primeras cartas de Magic, a partir de entonces el juego se extendió y hoy en dia aún goza de un buen número de seguidores. Para jugar sólo tienes que conocer las reglas, comprar unos cuantos sobres de cartas, y tener un contrincante. Y por supuesto, entre las criaturas de poder que uno puede barajar se encuentra la de nuestro amigo.




Via Distrito Magic The Gathering
Un poco de historia
Magic: The Gathering es un juego de estrategia y fantasía que se presenta en un formato de cartas coleccionables. Fue creado en 1993 por un professor de matemáticas de origen norteamericano llamado Richard Garfield. Magic supuso en su momento una revolución los juegos de fantasía, ya que se desmarcó completamente de los Juegos de Rol (o de personaje) que por entonces copaban el mercado. La empresa que lo comercializa se llama Wizards of the Coast y desde el lanzamiento del juego ha ido escalando posiciones hasta convertirse en uno de los referentes en EUA en lo que se refiere al juego de fantasía. En la actualidad, más de 7 millones de personas juegan a Magic en todo el mundo. Se distribuye en 55 países alrededor del globo y ha sido traducido a 10 idiomas, entre los cuales se encuentra el castellano. Atrae a jugadores de todas las edades y procedencias, además de a coleccionistas.
¿En qué consiste Magic: The Gathering? Magic: The Gathering es un juego de fantasía en que dos hechiceros se baten en un duelo mágico. Cada uno de ellos trae consigo su libro de hechizos (el mazo de cartas) con el cual deben intentar vencer a su contrincante. Esto se hace utilizando hechizos (cartas), que són elegidos por el jugador en función de su estilo de juego o su estrategia.
¿En qué consiste Magic: The Gathering? Magic: The Gathering es un juego de fantasía en que dos hechiceros se baten en un duelo mágico. Cada uno de ellos trae consigo su libro de hechizos (el mazo de cartas) con el cual deben intentar vencer a su contrincante. Esto se hace utilizando hechizos (cartas), que són elegidos por el jugador en función de su estilo de juego o su estrategia.
El juego se vende en formato de cartas coleccionables, en sobres que contienen unas cuántas de ellas agrupadas al azar. Cuando se compra un sobre, sólo se consiguen algunas de las cartas que se pueden utilizar en el juego. Las cartas són diferentes en función de su rareza: algunas són raras y otras són comunes. Es decir, algunas son más faciles de conseguir que otras. De alguna manera son una versión moderna de las colecciones de cromos.
A algunas personas lo que más les atrae de Magic son las ilustraciones de las cartas. De hecho, estas pueden ser coleccionadas como cromos o ilustraciones sólo por el placer de poseerlas, sin jugar jamás con ellas. Otros disfrutan con el juego a causa de las multiples combinatorias que ofrece la baraja. Hay muchas maneras possibles de crear-la dependiendo de la estrategia y el estilo del jugador y esto puede ser un reto muy interessante para cierto tipo de jugadores. Finalmente nos encontramos con aquellos participantes a los que les encanta competir, batirse y enfrentarse con contrincantes cada vez mejores.
En definitiva, Magic: The Gathering es un juego muy fácil de aprender, altamente adictivo y muy versátil. Además, su formato permite que sea altamente portátil, pudiendo jugar con él practicamente en cualquier parte.
Para saber más del funcionamiento del juego en la Wikipedia
Para saber más del funcionamiento del juego en la Wikipedia
Labels: Monstruos marinos
Poema de Peter Thorpe -I caught an octopus-
Published Monday, October 17, 2005 by Spyder.I caught an octopus, a small one, once,
While fishing off the docks in Puget Sound:
“What are you doing on my hook, you duce?”
I said, as all his tentacles flailed around
And thrashed and broke the surface with a fury.
“I’m trying to fish,” I said, “for cod and flounder.
Not some red rubbery freak. I’m in a hurry.
So please get off my hook. A Puget Sounder
Like me has more important things to do.”
But here the little octopus looked at me
With his sad eyes and said, “The trouble with you
And all your kind is that you think the sea
Owes you a life. You’re wrong. It owes you none
-Though you will cult these legs off, one by one.”
Peter Thorpe -Sonnets Two Ten-
Peter Thorpe
Peter Thorpe was born in Seattle. He is Professor Emeritus from the University of Colorado at Denver, where he was Chairman of the Denver Faculty Assembly and Chairman of the four-campus Faculty Council. He has published ten books and has been a book reviewer for the Denver Rocky Mountain News for twenty-five years. His poetry has appeared in the New Yorker, Antioch Review, College English, Northwest Review, West Coast Review, and elsewhere. During the nineteen-fifties he was an officer and aviator in the U.S. Navy, flying dive-bombers and jet fighters. He was in three aviation accidents. After his naval service he attended the University of Washington, receiving his Ph.D. in English in 1963. In his younger days he enjoyed mountain climbing in the Northwest, ascending such peaks as Mt. Adams, Mt. Hood, Mt. Rainier, and Mt. St. Helens (before it erupted). He has done volunteer work with United Way and various literacy programs. Peter Thorpe and his wife Nan divide their time between their home in Rancho Santa Fe, California, and their condo in Seattle.
Labels: Literatura, Poemas
Pulpo en el metro
Published Sunday, October 16, 2005 by Spyder.
Fotografía de shrocket
Pues para haber un pulpo sentado en el metro, todo parece la mar de normal...
Y cómo mañana hablaremos de Julio Cortázar...
"—Esto del tiempo es complicado, me agarra por todos lados. Me empiezo a dar cuenta poco a poco de que el tiempo no es como una bolsa que se rellena. Quiero decir que aunque cambie el relleno, en la bolsa no cabe más que una cantidad y se acabó. ¿Ves mi valija, Bruno? Caben dos trajes y dos pares de zapatos. Bueno, ahora imagínate que la vacías y después vas a poner de nuevo los dos trajes y los dos pares de zapatos, y entonces te das cuenta de que solamente caben un traje y un par de zapatos Pero lo mejor no es eso. Lo mejor es cuando te das cuenta de que puedes meter una tienda entera en la valija, cientos y cientos de trajes, como yo métela música en el tiempo cuando estoy tocando, a veces. La música y lo que pienso cuando viajo en el metro.
—Cuando viajas en el metro.—Eh, sí, ahí está la cosa —ha dicho socarrona mente Johnny—. El metro es un gran invento, Bruno. Viajando en el metro te das cuenta de todo lo que podría caber en la valija".
Julio Cortázar –El perseguidor-
—Cuando viajas en el metro.—Eh, sí, ahí está la cosa —ha dicho socarrona mente Johnny—. El metro es un gran invento, Bruno. Viajando en el metro te das cuenta de todo lo que podría caber en la valija".
Julio Cortázar –El perseguidor-
Labels: Literatura
Octopus Stencil -Octopus Dei-
Published Saturday, October 15, 2005 by Spyder.
El Opus Dei es una organización de la Iglesia católica que siempre suele generar comentarios de polémica (puesta de moda a partir del libro de El Código da Vinci). Para muchos catolicismo y poder no es algo que case demasiado bien, puesto que de siempre el poder suele corromper.
Muchas veces se utiliza el nombre de Octopus Dei, para denunciar los tentáculos de poder del Opus Dei que controla a empresas y personas de alto nivel.
PD. Sin embargo yo desde Mondopulpo tengo una nueva visión para el Octopus Dei... terriblemente atractiva.
Opus Dei
Algunas preguntas frecuentes sobre el Opus Dei, respondidas en su página web: http://www.opusdei.es/ . Iremos incorporando algunos artículos más sobre el tema y sobre su fundador.
¿Qué es el Opus Dei?
El Opus Dei es una Prelatura personal de la Iglesia Católica que ayuda a los fieles cristianos a buscar la santidad en y a través de sus actividades diarias, especialmente mediante el trabajo.
El Opus Dei fue fundado en 1928 por un joven sacerdote Católico de 26 años, Josemaría Escrivá, que murió en 1975 y fue beatificado por el papa Juan Pablo II en 1992.
El Opus Dei es una Prelatura personal de la Iglesia Católica que ayuda a los fieles cristianos a buscar la santidad en y a través de sus actividades diarias, especialmente mediante el trabajo.
El Opus Dei fue fundado en 1928 por un joven sacerdote Católico de 26 años, Josemaría Escrivá, que murió en 1975 y fue beatificado por el papa Juan Pablo II en 1992.
El Opus Dei es una "Prelatura personal". ¿Qué es eso?
Una Prelatura personal es una entidad jurídica dentro de la estructura jerárquica de la Iglesia, presidida por un Prelado y dependiente de la Sagrada Congregación de los Obispos, a la que pueden pertenecer laicos y clérigos. La erige la Santa Sede para fines pastorales u organizativos específicos, y está regulada por los estatutos que aprueba la Santa Sede. El término personal indica que se organiza y define por personas, de forma análoga a las diócesis y parroquias, que se organizan por áreas geográficas.
Para seguir leyendo algunas preguntas sobre el Opus Dei
Labels: Stencil
Mitología del pulpo -Islas Kiribati-
Published Thursday, October 13, 2005 by Spyder.Cerca de la Samoa de Stevenson, existe otro paraíso natural de la naturaleza, que constituyen las islas Kiribati, las cuales ocupan una extensión de casi 4000 Km de este a oeste, y unos cinco millones de Km2 de mucha agua y poca tierra .
Pues bien, en las islas Kiribati (también Islas Gilbert) existe un mito en el cual el dios pulpo (Na Kika) utilizó sus tentáculos para emerger la tierra del fondo del mar. El dios pulpo era uno de los hijos que tuvieron los primeros dioses, el dios piedra (Na Atibu) y la diosa del vacío (Nei Teuke).

La importancia del pulpo en el lenguaje Kiribati, queda patente en la multitud de palabras utilizadas para referirse a los pulpos.
Diccionario Kiribati-English
kao te kaonako: octopus.

La importancia del pulpo en el lenguaje Kiribati, queda patente en la multitud de palabras utilizadas para referirse a los pulpos.
Diccionario Kiribati-English
kao te kaonako: octopus.
kaonako: octopus.
kika: large octopus, octopus devil fish.
kíka: Octopus devilfish (jr).
kikabunia: small species of octopus.
kikao: small octopus.
mbembe: vent hole of octopus.
nikaro: octopus tied in coconut husk to be roasted without being damaged (e niraki ni karonaki).
Oriburibu n ainiku: a species of octopus with tentacles easily broken.
Labels: Mitología
Pulpos y música -Tango- ¡Leguisamo solo!
Published Wednesday, October 12, 2005 by Spyder.
¡Leguisamo solo!
M. H. Papávero
Alzan las cintas; parten los tungos
como saetas al viento veloz...
Detrás va el Pulpo, alta la testa
la mano experta y el ojo avizor.
Siguen corriendo; doblan el codo,
ya se acomoda, ya entra en acción...
Es el maestro el que se arrima
y explota un grito ensordecedor.
Leguisamo solo!...
gritan los nenes de la popular.
Leguisamo solo!...
fuerte repiten los de la oficial.
Leguisamo solo!...
ya esta el puntero del Pulpo a la par.
Leguisamo al trote!..
.y el Pulpo cruza el disco triunfal.
No hay duda alguna, es la muñeca,
es su sereno y gran corazón
los que triunfan por la cabeza
en gran estilo y con precisión.
Lleva los pingos a la victoria
con tal dominio de su profesión
que lo distinguen como una gloria,
M. H. Papávero
Alzan las cintas; parten los tungos
como saetas al viento veloz...
Detrás va el Pulpo, alta la testa
la mano experta y el ojo avizor.
Siguen corriendo; doblan el codo,
ya se acomoda, ya entra en acción...
Es el maestro el que se arrima
y explota un grito ensordecedor.
Leguisamo solo!...
gritan los nenes de la popular.
Leguisamo solo!...
fuerte repiten los de la oficial.
Leguisamo solo!...
ya esta el puntero del Pulpo a la par.
Leguisamo al trote!..
.y el Pulpo cruza el disco triunfal.
No hay duda alguna, es la muñeca,
es su sereno y gran corazón
los que triunfan por la cabeza
en gran estilo y con precisión.
Lleva los pingos a la victoria
con tal dominio de su profesión
que lo distinguen como una gloria,
mezcla de asombro y de admiración.
Habría que aclarar para entender este tango, que cuando el tango nombra a Leguisamo está haciendo referencia a jockey Irineo Leguisamo, la figura más importante que dio el turf rioplatense. Con un incontable número de carreras ganadas en los hipódromos fue apodado como el eximio, el maestro y ¡cómo no! también como el pulpo. El tango fue compuesto por el pianista Modesto Papavero y popularizada en la voz de Carlos Gardel.
Habría que aclarar para entender este tango, que cuando el tango nombra a Leguisamo está haciendo referencia a jockey Irineo Leguisamo, la figura más importante que dio el turf rioplatense. Con un incontable número de carreras ganadas en los hipódromos fue apodado como el eximio, el maestro y ¡cómo no! también como el pulpo. El tango fue compuesto por el pianista Modesto Papavero y popularizada en la voz de Carlos Gardel.
Labels: Música
Ojos del pulpo -The octopus as eyewitness-
Published Sunday, October 09, 2005 by Spyder.El artículo habla de un nuevo chip de silicio que tiene como modelo la retina de un pulpo. La visión del pulpo por el profesor Albert Titus fue estudiada profundamente, al considerarla que era una visión bien desarrollada pero con un sistema menos complejo que el de los vertebrados, lo que facilitaba su simulación. En el futuro cercano este chip servirá para cámaras que tengan que actuar en condiciones desfavorables para el ojo humano.
The Octopus as Eyewitness
The Octopus as Eyewitness
Michelle Delio
Sep, 26, 2003
Vía Wired News
Robots and people may soon be looking at the world through octopus eyes.
Albert Titus, an assistant professor of electrical engineering at the University at Buffalo, New York, has created a silicon chip that mimics the structure and functionality of an octopus retina.
His "o-retina" chip can process images just like an octopus eye does. The chip could give sight to rescue or research robots, allowing them to see more clearly than human eyes can in dark or murky conditions.
But Titus isn't content to merely replicate the functioning of a specific retina. His ultimate goal is to build a complete artificial vision system, including a brain that mimics the visual systems of various animals, so humans can look at the world differently.
Titus also hopes this system will eventually allow him to connect different "eyes" to different "brains" -- allowing, for example, a lion's brain to process images as seen by an eagle's retina.
"The visual system is more than eyes," Titus said. "An animal uses eyes to see, but the brain to perceive. Yet, the retina is an extension of the brain, so where does the distinction between seeing and perceiving begin and end?"
Titus intends to find out.
He and his team have already developed the beginning of what will eventually become the o-retina's brain -- two neural-network algorithms that will process visual information from the o-retina chip. Neural networks are designed to imitate the ways that human or animal brains process information.
The o-retina system might also be able to utilize a human user's brain. O-retina chips could be placed into a head-mounted computer display that would process images as an animal's eyes would. The human would be able to view this visual data in real time.
But such a system wouldn't produce exactly the same images that an animal sees, since the image would be seen by a human through human eyes before going to the brain. Still, Titus believes such a system could be used to enhance human vision, and would certainly provide a different view of the world.
"Computerized devices that enhance vision are already in use for specific medical conditions that lenses and surgery can't correct," said optometrist John Markham. "Incorporating the visual abilities of other animals into such a system could be potentially useful for some medical conditions. And it would certainly be interesting to see the world through other creatures' eyes."
The o-retina chip is a silicon CMOS-based integrated circuit, the same sort of chip that's used in computer microprocessors. But the o-retina is based on 1.6-micron technology, about 10 times larger than the newest microprocessor transistors.
Titus said he opted to replicate an octopus retina because octopuses have a complex nervous system and well-developed visual system, but not as complex as vertebrates' systems, which makes the octopus' system easier to study.
The o-retina chip relies on brightness, size, orientation and shape to distinguish objects, just as an octopus does.
Octopus eyes function like the lens of a camera, with a biological lens that moves inward to the retina to focus close up, and outward to focus on distant objects. In vertebrates, the lens of an eye has a fixed focus, and must change shape to focus on objects that are near or far. So depending on what the eye is focused on, objects at other distances will not be in sharp focus.
Future versions of the o-retina chip will include polarization sensitivity -- the ability to see polarized light, particularly underwater -- an important aspect of the octopus' visual system.
The o-retina project began two years ago and is still a work in progress. Titus refers to the current o-retina chip as the "first revision."
Titus has also designed a silicon retina chip that mimics the process of edge detection, a type of data compression performed by biological eyes. With edge detection, the retina reduces the amount of visual information it takes in, extracting and processing only the most useful information.
This chip can identify objects by processing visual information only from the edges of an image rather than the whole picture. Edge information usually is sufficient for detecting and tracking objects, Titus said. In robots, this chip could allow for faster processing of visual data.
O-retina chip research is funded by the National Science Foundation.
Labels: Características
Arte y pulpos -Fred Kyrel-
Published Friday, October 07, 2005 by Spyder.Si no fuera por algunos detalles femeninos, pensaría que el movimiento gay ya forma parte de la iconografía pulpera. Aunque de una forma u otra estas imágenes tienen algo de esto, por la parte andrógina que le toca a la modelo.



Para visitar la página del fotógrafo Fred Kyrel aquí (Recomiendo no saltarse la presentación)
Fred Kyrel
I'm a french photographer based in Metz who like models with alternative and fetish looks.I love creating colored atmospheres, strange with some contrast and a humoristic touch and images that brings emotions.
My website : http://www.kyrel.net
Myspace : http://www.myspace.com/
FredkyrelGallery in : http://www.sugarcut.com
Pulpos en la Ciencia Ficción -Modelos de naves espaciales-
Published Thursday, October 06, 2005 by Spyder.La primera es la foto del modelo de la nave espacial que supuestamente se conserva en Roswell (Nuevo México) desde 1947. La segunda es la foto enviada por uno de nuestros lectores, de un nuevo avistamiento que pudo presenciar hace apenas una década (el testimonio de su posterior abducción lo hemos enviado a Milenio 3).
Podemos comprobar que los extraterrestres han mejorado sus utilitarios en apenas unas pocas décadas.

Podemos comprobar que los extraterrestres han mejorado sus utilitarios en apenas unas pocas décadas.

Otro dato muy curioso es que los extraterrestres aparcan sus naves al lado de las casas, lo cual demuestra un civismo encomiable.


La invasión está cerca!!!
Labels: Ciencia Ficción, Fotografías, Humor
Cocina -Pulpo con garbanzos-
Published Monday, October 03, 2005 by Spyder.
INGREDIENTES:
1/4 Kg. de garbanzos.
1/2 Kg. de pulpo.
Acelgas.
6 dientes de ajo.
1 pimiento seco.
1 cebolla.
1 tomate grande maduro.
1 pimiento verde.
Azafrán.
Sal.
PREPARACIÓN:
1/4 Kg. de garbanzos.
1/2 Kg. de pulpo.
Acelgas.
6 dientes de ajo.
1 pimiento seco.
1 cebolla.
1 tomate grande maduro.
1 pimiento verde.
Azafrán.
Sal.
PREPARACIÓN:
Se pone el pulpo con los garbanzos y las acelgas a cocer. Se fríe el pimiento rojo y se maja junto con los ajos crudos en el mortero. En la sartén se hace un refrito con la cebolla, el tomate y el pimiento verde, una vez hecho se le añade el aliño del mortero y se marea un poco después de lo cual se agrega a la olla donde hemos cocido el pulpo. Se se quiere se pueden poner unas patatas.
RECETA DE: Namor
Labels: Gastronomía, Recetas
Pulpo's Tattoo V
Published Saturday, October 01, 2005 by Spyder.
El típico dibujo de un pulpo gigante atacando a un mono y un pájaro alcohólico. Que me lo expliquen...
Labels: Tatuajes



